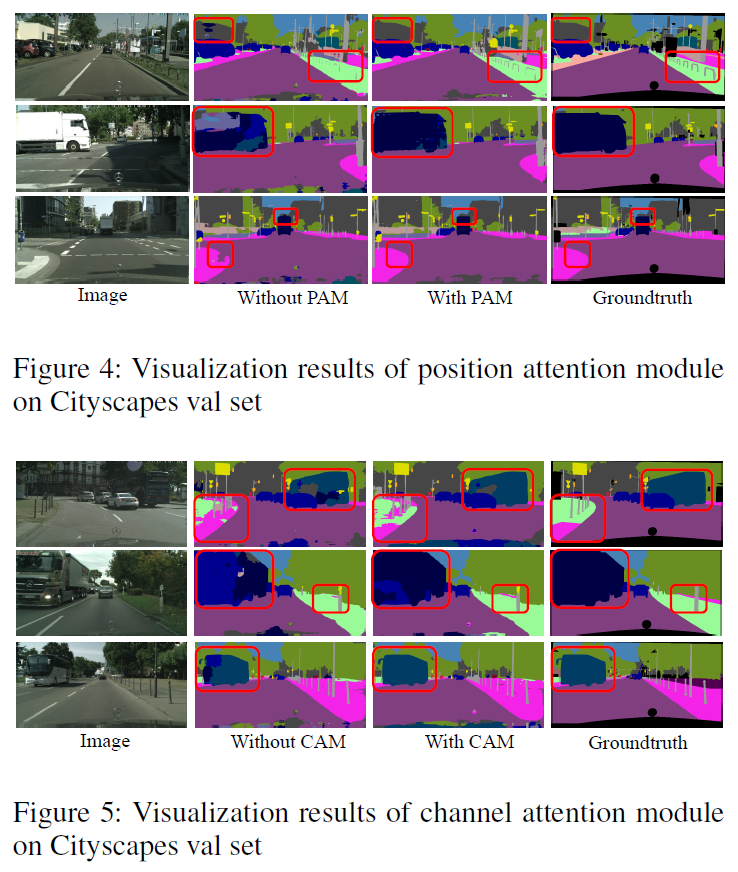
“Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation” improves scene segmentation tasks performance by attaching self-attention mechanism. It is in arxiv yet and the authors are from CASIA IVA.
Summary
- Problem Statement
- Given a picture of scene segmentation, stuff or objects, are diverse on scales, lighting, and views.
- Since convolution operations have a local receptive field, the features corresponding to the pixels with the same label do have some differences.
- These differences affect the recognition accuracy of traditional FCNs.
- Research Objective
- Address the scene segmentation task by capturing rich contextual dependencies based on the self-attention machanism.
- Proposed Solution
- Unlike previous works that capture contexts by multi-scale features fusion, the paper proposes a Dual Attention Networks (DANet) to adaptively integrate local features with their global dependencies.
- Append two types of attention modules on top of traditional dilated FCN, chich model the semantic interdependencies in spatial and channel dimensions respectively.
- The position attention module selectively aggregates the features at each position by a weighted sum of the features at all positions.
- The channel attention module selectively emphasizes interdependent channel maps by integrating associated features among all channel maps.
- Two attention modules are added to further improve feature representation which contributes to more precise segmentation results.
- Contribution
- Propose a Dual Attention Network (DANet) to capture the global feature dependencies in the spatial and channel dimensions for the task of scene understanding.
- A position attention module is proposed to learn the spatial interdependencies of features and a channel attention module is designed to model channel interdependencies. It significantly improves the segmentation results by modeling rich contextual dependencies over local features.
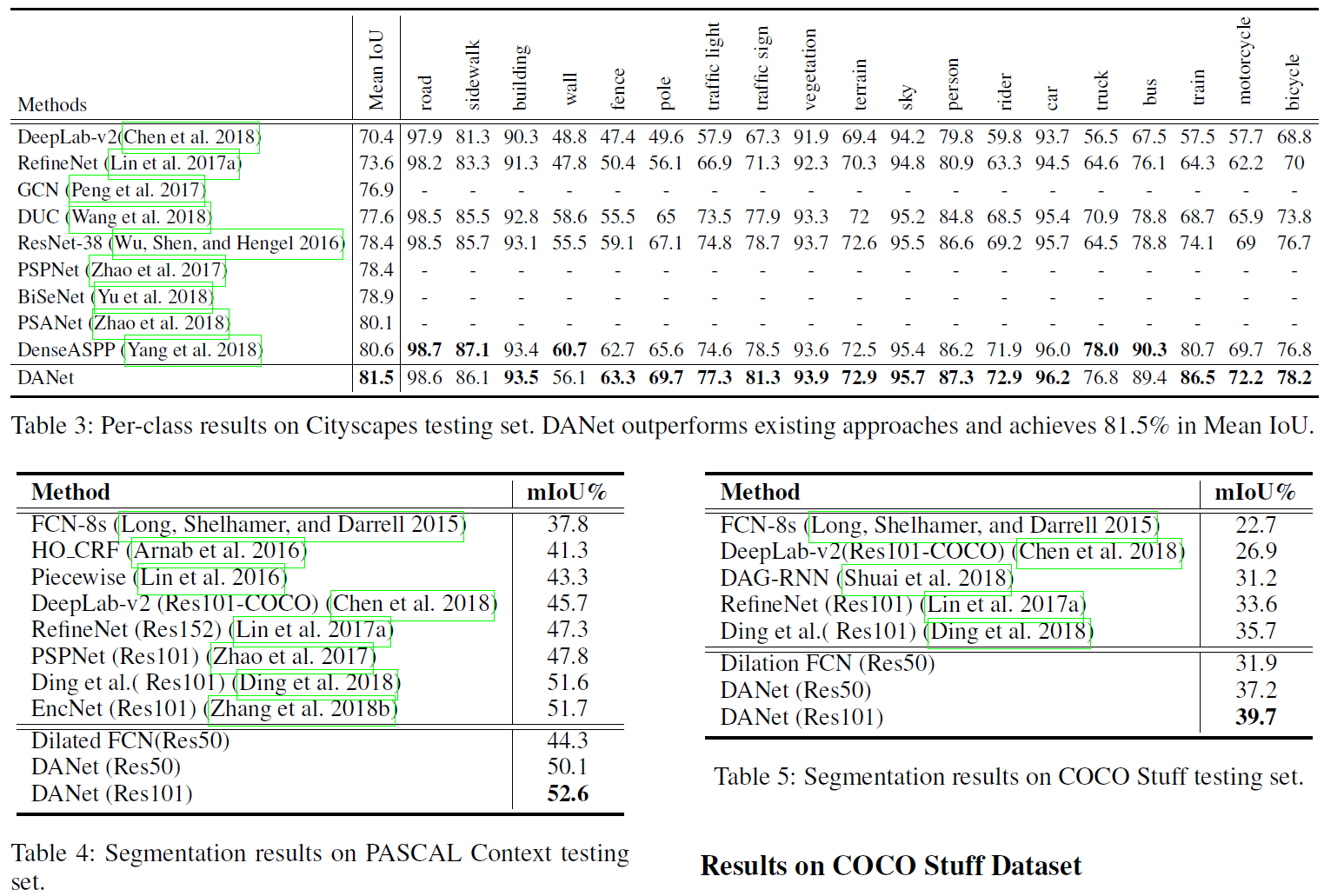
- Achieve new state-of-the-arts results on Cityscapes dataset, PASCAL Context dataset, and COCO Stuff dataset.
Dual Attention Network
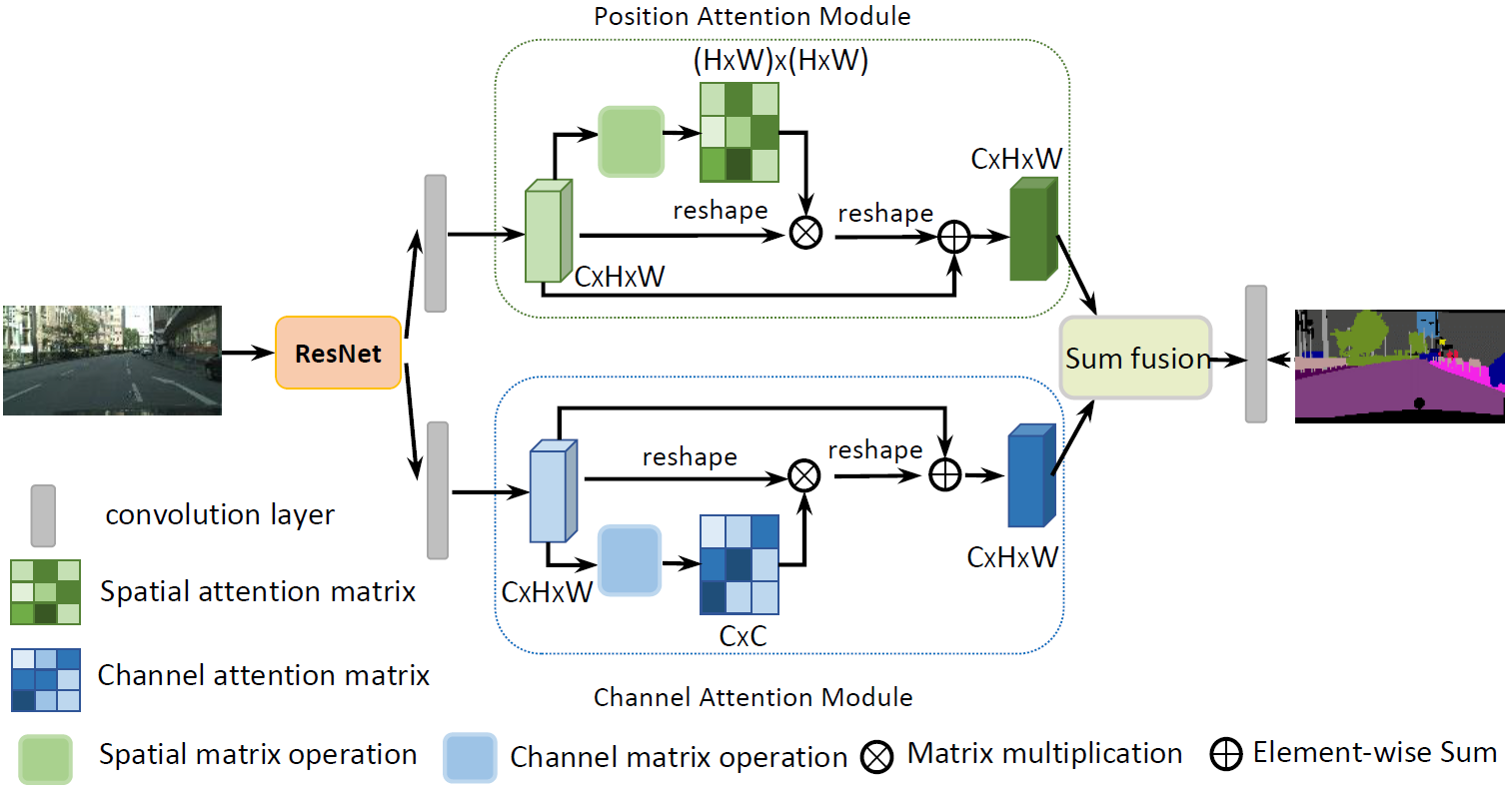
Figure 1: An overview of the Dual Attention Network.
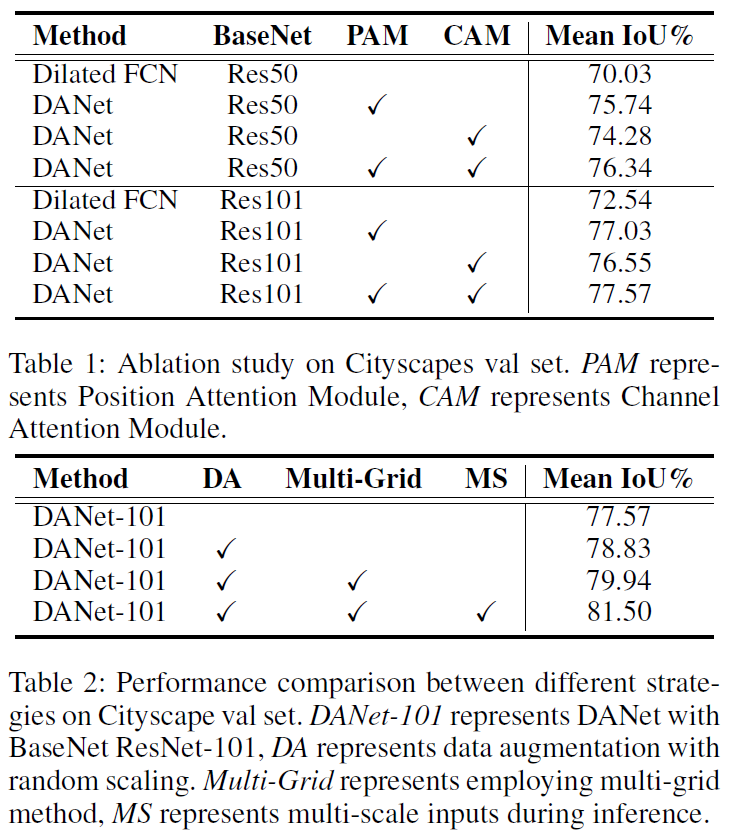
There are two types of attention modules to draw global dependencies over local features generated by a dilated residual network, thus obtaining better feature representations for pixel-level prediction. In the DRN, the authors remove the downsampling operations and employ dilation convolutions in the last two ResNet blocks, thus enlarging the size of the final feature map size to 1/8 of the input image. Then the features from the dilated residual network would be fed into two parallel attention modules: position attention module and channel attention module.
Finally we aggregate the output features from the two attention modules to obtain better feature representations for pixel-level prediction.
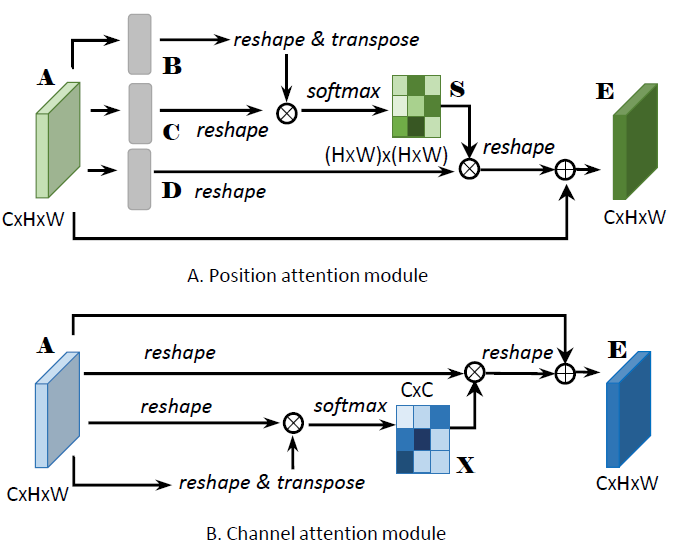 Figure 2: The details of Position Attention Module and Channel Attention Module are illustrated in (A) and (B).
Figure 2: The details of Position Attention Module and Channel Attention Module are illustrated in (A) and (B).
Self-Attention
Self-attention, also called intra-attention, calculates the response at a position in a sequence by attending to all positions within the same sequence.
\[Attention(Q,K,V) = softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V\]- \(Q\):Query, \(K\):Key, \(V\):Value
- \(Q=K=V\).
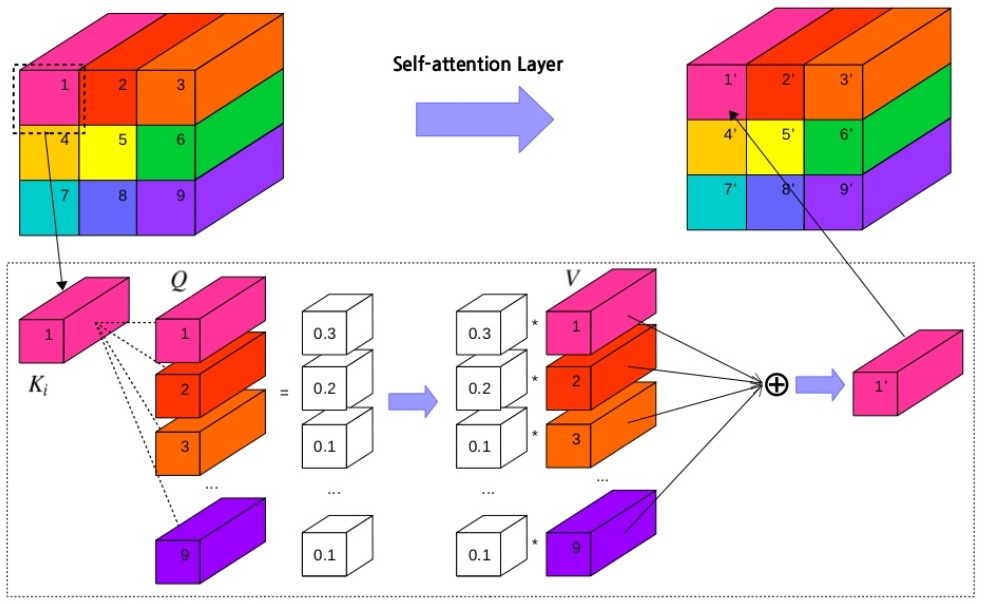 Figure 3: Self attention mechanism.
Figure 3: Self attention mechanism.
Position Attention Module
The position attention module encodes a wider range of contextual information into local features, thus enhancing their representative capability.
First, apply a convolution layer to obtain the features of dimension reduction. Second, feed the features into the position attention module and generate new features of spatial long-range dependencies through the following three.
- Generate a spatial attention matrix which models the spatial relationship between any two pixels of the features.
- Perform a matrix multiplication between the attention matrix and the original features.
- Perform an element-wise sum operation on the above multiplied resulting matrix and original features to obtains the final representations reflecting long-range contexts.
Resulting feature at each position is a weighted sum of the features at all positions and original features.
Channel Attention Module
Channel long-range dependencies are captured by a channel attention module. By exploiting the interdependencies between channel maps, we could emphasize interdependent feature maps and improve the feature representation of specific semantics.
The process to capture the channel relationship is similar to the position attention matrix is calculated in the channel dimension.
\[x_{ji}=\frac{exp(A_i \cdot A_j)}{\sum_{i=1}^Cexp(A_i \cdot A_j)} \\ E_j = \beta \sum_{i=1}^C(x_{ji}A_i)+A_j\]The final feature of each channel is a weighted sum of the features of all channels and original features, which models the long-range semantic dependencies between feature maps.
Attention Module Embedding with Networks
We transform the outputs of two attention modules by a convolution layer and perform an element-wise sum to accomplish feature fusion. At last a convolution layer is followed to generate the final prediction map.
Experiments