This post is a summary and paper skimming on image retrieval related research. So, this post will be keep updating by the time.
Paper List
Feature Representation
- Large-Scale Image Retrieval with Attentive Deep Local Features, ICCV2017
- Efficient diffusion on region manifolds: recovering small objects with compact CNN representations, CVPR2017
- Particular object retrieval with integral max-pooling of cnn activations (RMAC), ICLR2016
Metric Learning
- Improved deep metric learning with multi-class N-pair loss objective, NIPS2016
- Deep image retrieval: learning global representations for image search, ECCV2016
- End-to-end learning of deep visual representations for image retrieval, IJCV2017
- It is an extended version of ECCV2016 paper “Deep image retrieval: learning global representations for image search”
Large-Scale Image Retrieval with Attentive Deep Local Features
- Conference: ICCV2017
Summary
- Problem Statement
- Performance of CNN-based global descriptors for image retrieval may be hindered by a wide variety of challenging conditions observed in large-scale datasets, such as clutter, occlusion, and variations in viewpoint and illumination.
- Global descriptors lack the ability to find patch-level matches between images.
- As a result, it is difficult to retrieve images based on partial matching in the presence of occlusion and background clutter.
- CNN-based local features are proposed for patch-level matching.
- However, these techniques are not optimized specifically for image retrieval since they lack the ability to detect semantically meaningful features, and show limited accuracy in practice.
- Performance of CNN-based global descriptors for image retrieval may be hindered by a wide variety of challenging conditions observed in large-scale datasets, such as clutter, occlusion, and variations in viewpoint and illumination.
- Research Objective
- To develop a large-scale image retrieval system based on a novel CNN-based feature descriptor
- Proposed Solution
- Propose an attentive local feature descriptor suitable for large-scale image retrieval, referred to as DELF (DEep Local Feature)
- The new feature is based on convolutional neural networks, which are trained only with image-level annotations on a landmark image dataset.
- To identify semantically useful local features for image retrieval, we also propose an attention mechanism for keypoint selection, which shares most network layers with the descriptor.
- This framework can be used for image retrieval as a drop-in replacement for other keypoint detectors and descriptors, enabling more accurate feature matching and geometric verification.
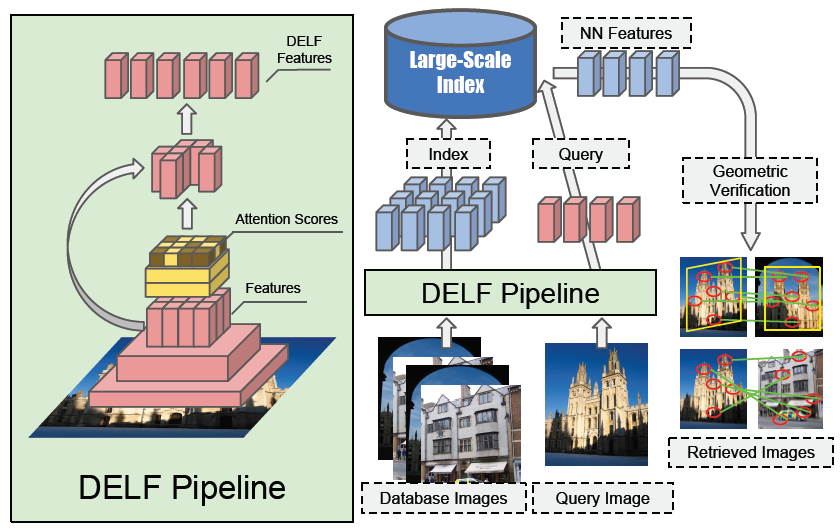 Figure: Overall architecture of DELF. On the left, it illustrate the pipeline for extraction and selection of DELF. On the right, it illustrates large-scale feature-based retrieval pipeline. DELF for database images are indexed offline. The index supports querying by retrieving nearest neighbor (NN) features, which can be used to rank database images based on geometrically verified matches.
Figure: Overall architecture of DELF. On the left, it illustrate the pipeline for extraction and selection of DELF. On the right, it illustrates large-scale feature-based retrieval pipeline. DELF for database images are indexed offline. The index supports querying by retrieving nearest neighbor (NN) features, which can be used to rank database images based on geometrically verified matches.
- Contribution
- Proposed system produces reliable confidence scores to reject false positives, in particular, it is robust against queries that have no correct match in the database.
- The evaluation in Google-Landmarks dataset shows that DELF outperforms existing global and local descriptors by substantial margins.
- The evaluation in existing datasets shows that DELF achieves excellent performance when combined with global descriptors.
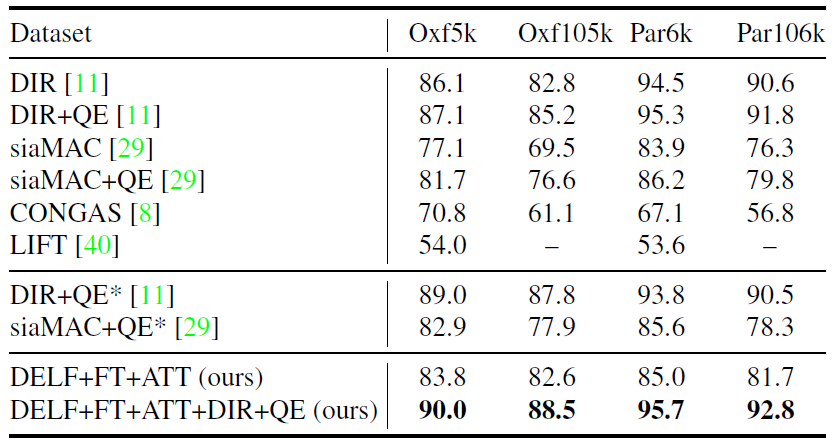 Figure: Performance evaluation on existing datasets in mAP (%). All results of existing methods are based on our reproduction using public source codes. We tested LIFT only on Oxf5k and Par6k due to its slow speed. ( denotes the results from the original papers.)*
Figure: Performance evaluation on existing datasets in mAP (%). All results of existing methods are based on our reproduction using public source codes. We tested LIFT only on Oxf5k and Par6k due to its slow speed. ( denotes the results from the original papers.)*
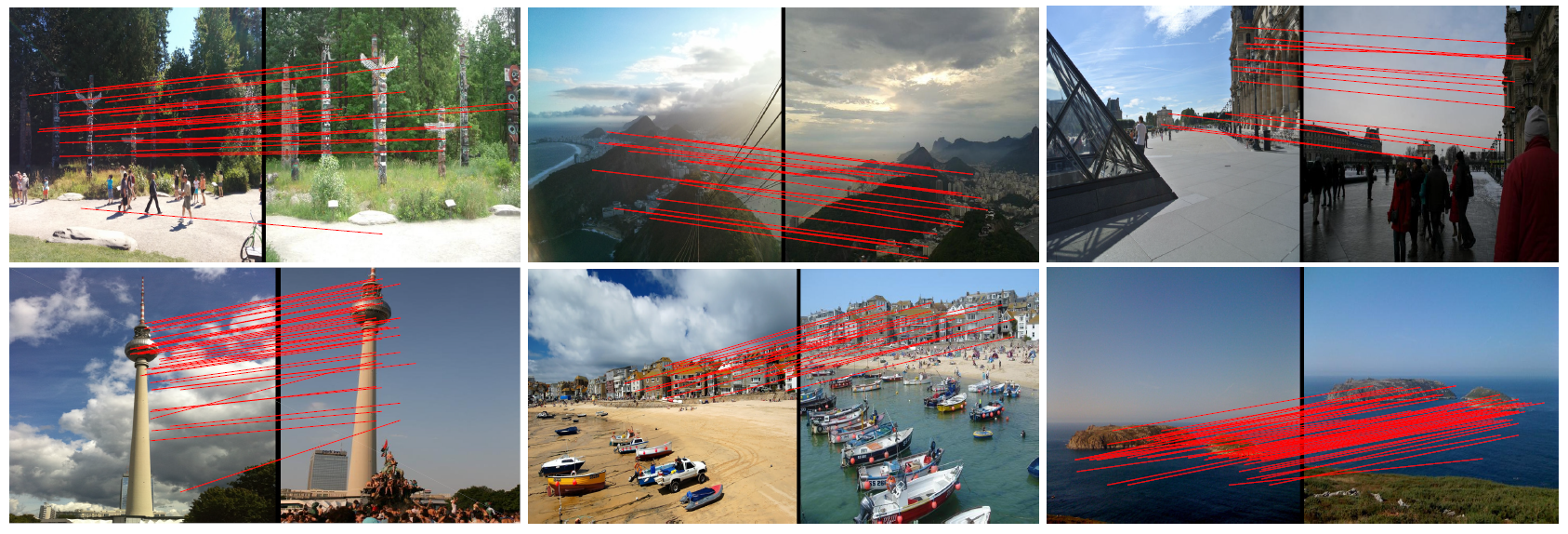

Figure: Visualization of feature correspondences between images in query and database using DELF+FT+ATT. DELF successfully matches landmarks and objects in challenging environment including partial occlusion, distracting objects, and background clutter.
References
Efficient diffusion on region manifolds
- Title: Efficient diffusion on region manifolds: recovering small objects with compact CNN representations
- Conference: CVPR2017
Summary
- Problem Statement
- Query expansion is a popular method to improve the quality of image retrieval with both conventional and CNN representations.
- It has been so far limited to global image similarity.
- Research Objective
- Focuses on diffusion, a mechanism that captures the image manifold in the feature space.
- Proposed Solution
- The diffusion is carried out on descriptors of overlapping image regions rather than on a global image descriptor.
- An efficient off-line stage allows optional reduction in the number of stored regions.
- In the on-line stage, the proposed handling of unseen queries in the indexing stage removes additional computation to adjust the precomputed data.
- We perform diffusion through a sparse linear system solver, yielding practical query times well below one second.
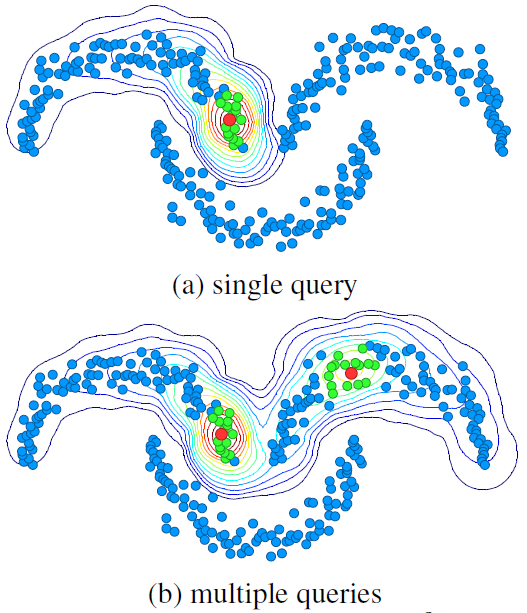 Figure:(Top): Diffusion on a synthetic dataset in \(\mathbb{R}^2\). Dataset points, query points and their k-nearest neighbors are shown in blue, red, and green respectively. Contour lines correspond to ranking scores after diffusion. In this work, points are region descriptors.
Figure:(Top): Diffusion on a synthetic dataset in \(\mathbb{R}^2\). Dataset points, query points and their k-nearest neighbors are shown in blue, red, and green respectively. Contour lines correspond to ranking scores after diffusion. In this work, points are region descriptors.
- Contribution
- Introduce a regional diffusion mechanisum, which handles one or more query vectors at the same cost. This approach significantly improves retrieval of small objects and cluttered scenes.
- A new approach to unseen queries with no computational overhead is proposed.
- Experimentally, it gives a significant boost in performance of image retrieval with compact CNN descriptors on standard benchmarks, especially when the query object covers only a small part of the image.
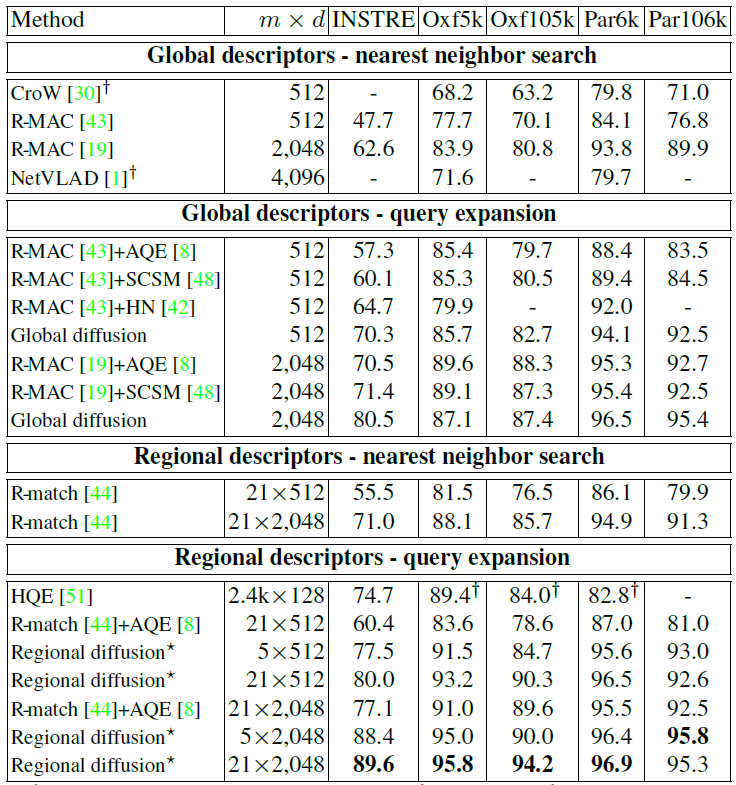 Figure:(Top): Performance comparison to the state of the art. Points at 512D are extracted with VGG and at 2048D with
ResNet101 . Regional diffusion with 5 regions uses GMM.
Figure:(Top): Performance comparison to the state of the art. Points at 512D are extracted with VGG and at 2048D with
ResNet101 . Regional diffusion with 5 regions uses GMM.

Figure: Query examples from INSTRE, Oxford, and Paris datasets and retrieved images ranked by decreasing order of ranking difference between global and regional diffusion. We measure precision at the position where each image is retrieved and report this under each image for global(red) and regional(blue) diffusion. Average Precision (AP) is reported per query for the two methods.
References
- Paper: Efficient diffusion on region manifolds: recovering small objects with compact CNN representations
- Code: Matlab
R-MAC
- Title: Particular object retrieval with integral max-pooling of cnn activations
- Conference: ICLR2016
Summary
- R-MAC
- It aggregates several image regions into a compact feature vector of fixed length and is thus robust to scale and translation.
- This representation can deal with high resolution images of different aspect ratios and obtains a competitive accuracy.