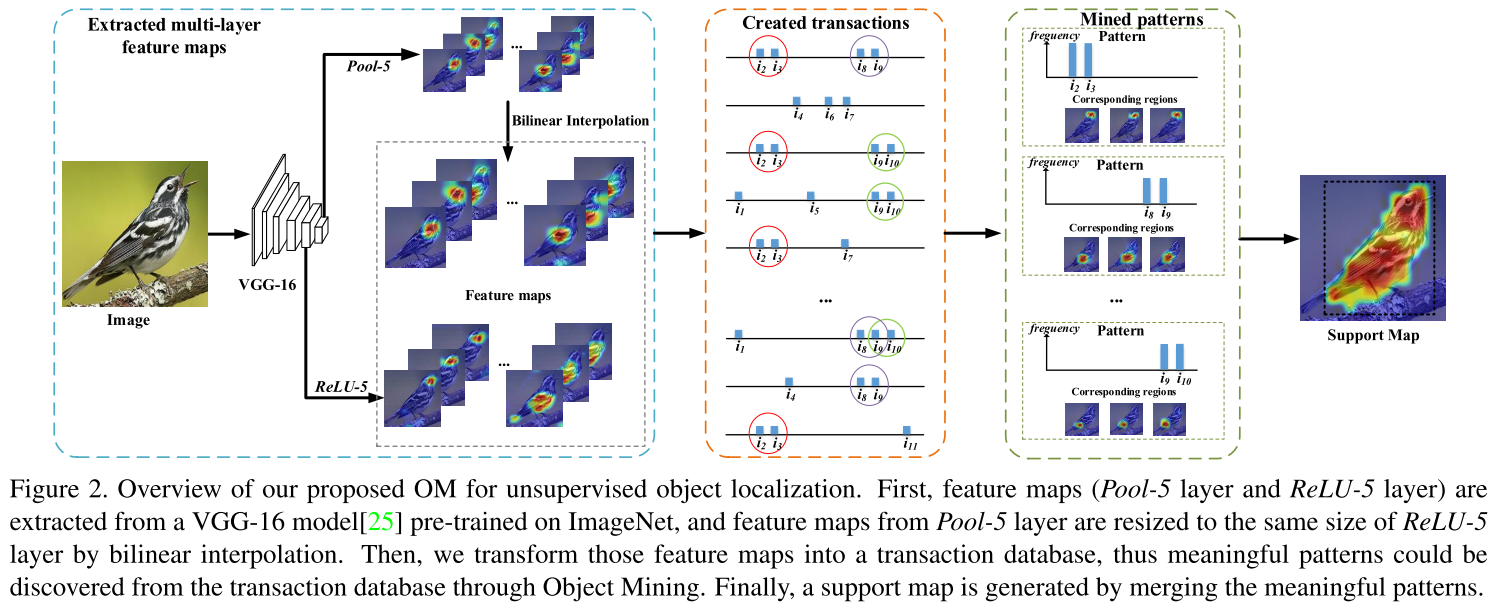
When we solve machine learning problem, we have to optimize a certain objective function. One of the case of it is convex optimization problem which is a problem of minimizing convex functions over convex sets.
Optimization Problem
In mathematics and computer science, an optimization problem is the problem of finding the best solution from all feasible solutions.
We can write the standard form of a optimization problem as,
The function \(f(x)\) is an objective function to be minimized over the variable \(x\), and both functions \(g_i(x)\) and \(h_i(x)\) are constraints function. If the optimization is maximization problem, it can be treated by negating the objective function. We can think of it as finding an optimum point which can be the minimum or maximum point of the objective function. Sadly, we can not find optimum point in every case. The simplest way to find the optimum point is to find zero point of its derivative function, however, there can be non-differentiable functions or it can not be a extreme point even though it is zero point, such as saddle point. And one of the easy case to find the extreme point is convex optimization.
Convex Set and Convex Function
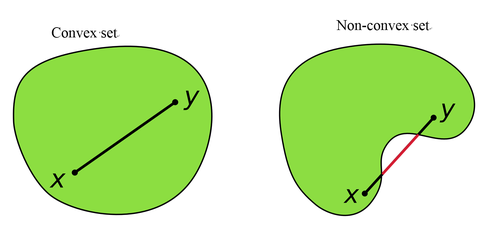
Convex set includes a convex region where, for every pair of points within the region, every point on the straight line segment that joins the pair of points is also within the region.
In mathematics, a convex function is if its epigraph (the set of points on or above the graph of the function) is a convex set.
In other word, The convex function has convex set as a domain of it such as the quadratic function \(x^{2}\) and the exponential function \(e^{x}\). The convex function can be written as,
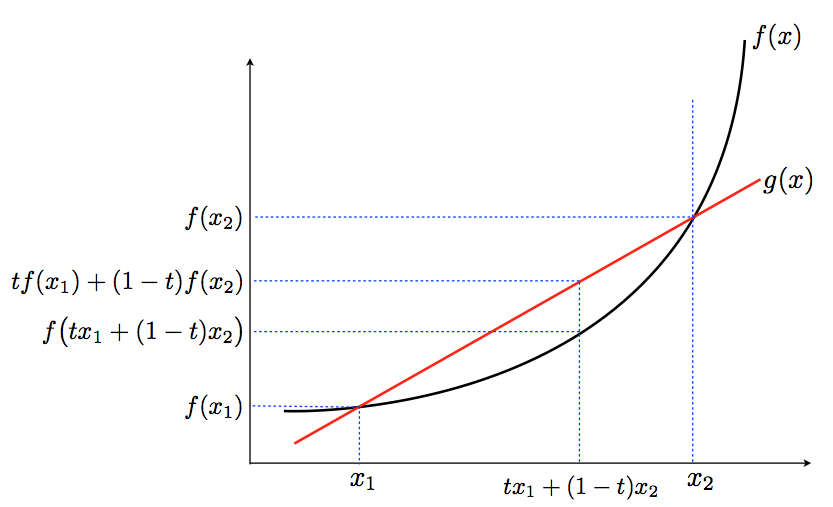
The reason why convex function is important on optimization problem is that it makes optimization easier than the general case since local minimum must be a global minimum. In other word, the convex function has to have only one optimal value, but the optimal point does not have to be one. The below loosely convex function has one optimal value with multiple optimal points.
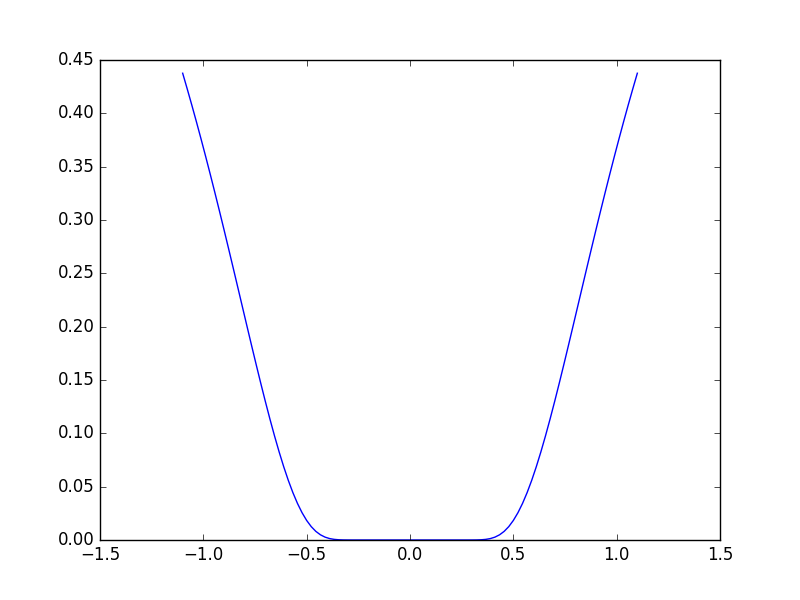
If you want to make it one optimal value with only one optimal point, you can put more condition as below.
This function is called strictly convex function and we can design an optimization algorithm since it has unique optimal point.
Convex Optimization Problem
Convex optimization problem is to find an optimal point of a convex function defined as,
when the functions \(f, g_1 \ldots g_m : \mathbb{R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) are all convex functions. As I mentioned about the convex function, the optimization solution is unique since every function is convex. There are well-known algorithms for convex optimization problem such as, gradient descent method, lagrange multiplier, and newton method.