Learn about stack, queue, dequeue, its implementation and running time.
Stack
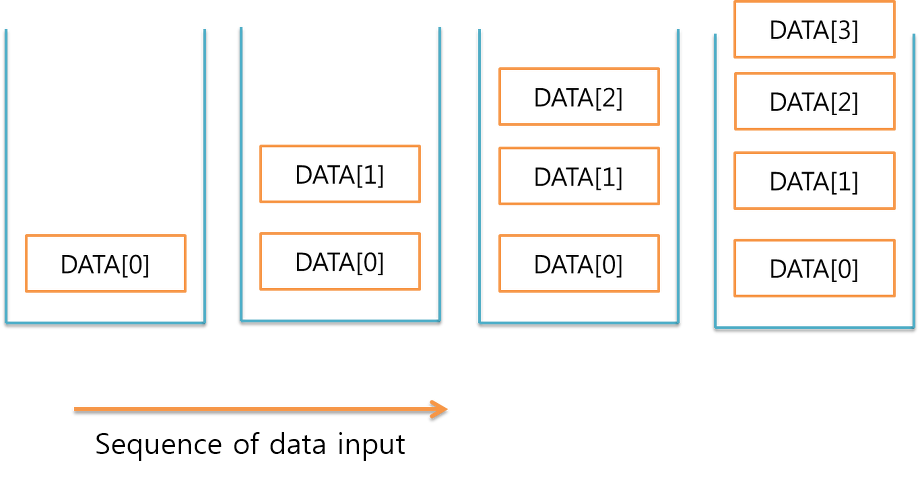
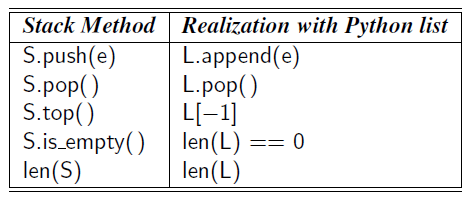
- Stack: a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the last-in, first-out (LIFO) principle.
Operations
- S.push(e): Add element e to the top of stack S.
- S.pop(): Remove and return the top element from the stack S
- S.top(): Return a reference to the top element of stack S, without removing it.
- S.is_empty(): Return True if stack S does not contain any elements.
- len(S): Return the number of elements in stack S.
Use list as stack in Python
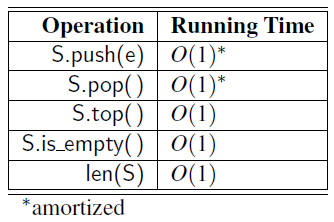
Time Complexity
- Time complexity of array-based stack implementation
- The bounds for push and pop are amortized due to similar bounds for the list class.
- The space using is \(O(n)\), where \(n\) is the current number of elements in the stack.
Queue
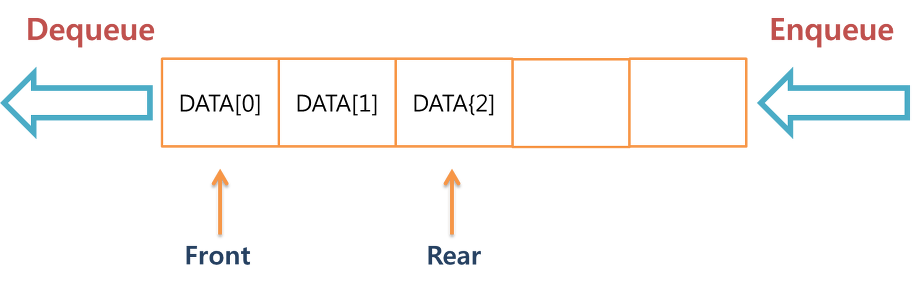
- Queue: a collection of objects that are inserted and removed according to the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle.
Operations
- Q.enqueue(e): Add element e to the back of queue Q.
- Q.dequeue(): Remove and return the first element from the queue Q.
- Q.first(): Return a reference to the first element of queue Q, without removing it.
- Q.is_empty(): Return True if queue Q does not contain any elements.
- len(Q): Return the number of elements in queue Q.
Queue in Python
- Using list as queue in python is possible but not efficient because all of the other elements have to be shifted by one after inserts or pops
- To implement queue, use ‘collections.deque’ which was designed to have fast appends and pops.
from collectinos import deque queue = dequeue(["Eric", "John", "Michael"]) queue.append("Terry") # Q.enequeue(e) queue.popleft() # Q.dequeue() queue[0] # Q.first() len(queue)==0 # Q.is_empty() len(queue) # len(Q)
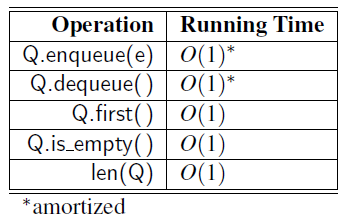
Time Complexity
- Time complexity of array-based queue implementation
- The bounds for enqueue and dequeue are amortized due to the resizing of the array.
- The space using is \(O(n)\), where \(n\) is the current number of elements in the queue.
Double-Ended Queue
- Double-Ended Queue (deque): a queue-like data structure that supports insertion and deletion at both the front and the back of the queue.
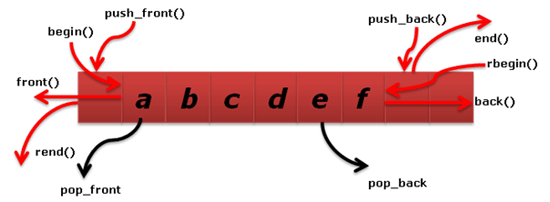
Operations
- D.add_first(e): Add element e to the front of deque D.
- D.add_last(e): Add element e to the back of deque D.
- D.delete_first(): Remove and return the first element from the deque D.
- D.delete_last(): Remove and return the last element from the deque D.
- D.first(): Return a reference to the first element of deque D, without removing it.
- D.last(): Return a reference to the last element of deque D, without removing it.
- D.is_empty(): Return True if deque D does not contain any elements.
- len(D): Return the number of elements in deque D.
Deques in the Python Collections Module
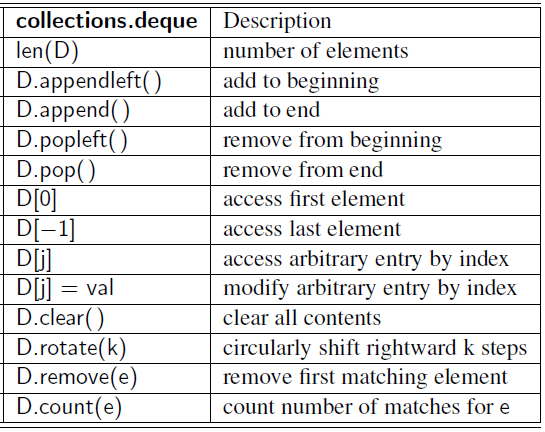
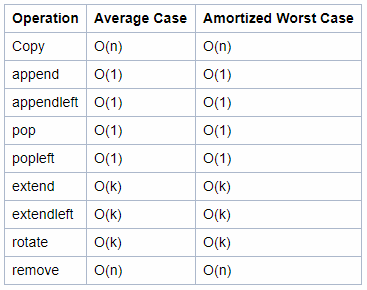
Time Complexity
- ‘n’ is the number of elements currently in the container. ‘k’ is either the value of a parameter or the number of elements in the parameter.
Quiz
Stack related quiz Game of Two Stacks in HackerRank
Answer code in Python 3
#!/bin/python3
import sys
g = int(input().strip())
for a0 in range(g):
n,m,x = input().strip().split(' ')
n,m,x = [int(n),int(m),int(x)]
a = list(map(int, input().strip().split(' ')))
b = list(map(int, input().strip().split(' ')))
# your code goes here
sum = 0
count = 0
max_count =0
tempA = []
# Inverse 'a' and 'b' list to use as stack
a.reverse()
b.reverse()
# Pop from stack A and sum until it exceeds the limit
while len(a)!=0:
if sum + a[-1] <= x:
sum += a[-1]
count += 1
tempA.append(a.pop()) # Save pop-ed element from stack A
else:
break
max_count = count # Save current max_count
# Pop from stack B and plus it with 'sum'
while len(b)!=0:
sum += b.pop()
count += 1
# If 'sum' exceeds the limit, discard one from tempA
while sum > x and len(tempA)!=0:
sum -= tempA.pop()
count -= 1
if sum <= x and max_count < count:
max_count = count
elif sum > x:
break
print (max_count)