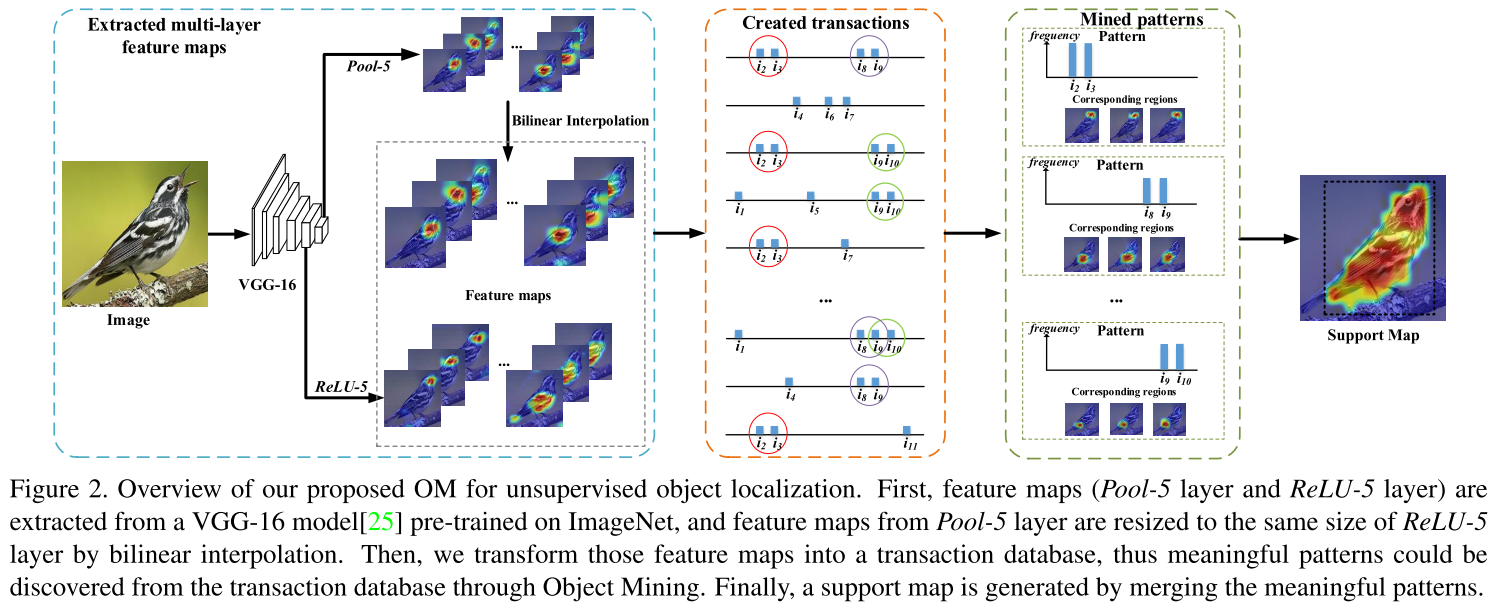
Learn about hash table, hash function, hash code, its implementation and running time.
Hash Table
- Hash table: a data structure that maps keys to values for highly efficient lookup.
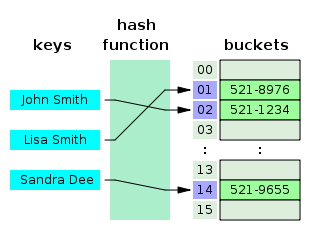
- Hash function: to map general keys to corresponding indices in a table
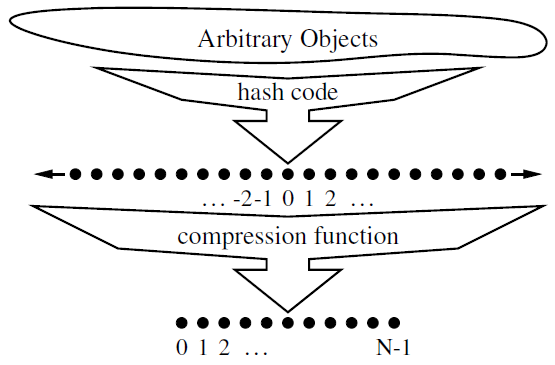
- The goal of a hash function is to map each key \(k\) to an integer in the range \([0,N-1]\).
- Two parts of a hash function: a hash code and a compression function
- Hash code: maps a key \(k\) to an integer
- Compression function: maps the hash code to an integer within a range of indices for a bucket array
- Bucket array: an array where each index obtains a bucket of collection of items for two different keys with the same index
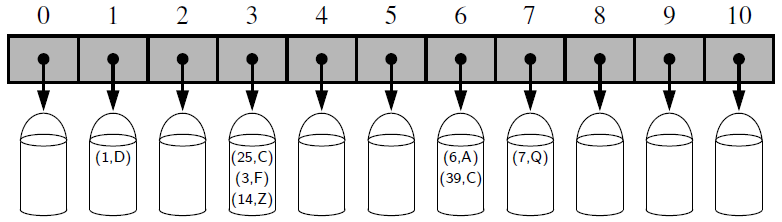
- Collision: if there are two or more keys with the same hash value, then two different items will be mapped to the same bucket and a collision has occurred.
- Hash function: to map general keys to corresponding indices in a table
Implementation
- For the simple implementation, we use an array of linked lists and a hash code function.
- Compute the key’s hash code (Two different keys could have the same hash code)
- Map the hash code to an index in the array (Two different hash codes could map to the same index)
- Store the key and value in the index. (Use linked list because of collision)
- To retrieve the value pair by its key, repeat the same process
- Compute the hash code from the key
- Compute the index from the hash code
- Search through the linked list for the value with this key
Running Time
- Comparison of the running times between unsorted list and hash table where \(n\) denote the number of items in the map.
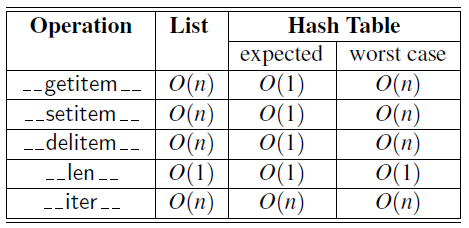
- If the number of collisions is very high, the worst case is \(O(n)\) and it is \(O(1)\) for minimum collisions.
- Alternatively, hash table can be implemented with a balanced binary search tree.
- It gives \(O(\log N)\) lookup time.
- It potentially uses less space and is able to iterate through the keys in order, which can be useful sometimes.
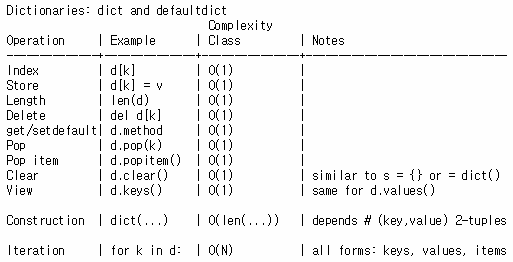
- Time complexity of dictionary in Python
Quiz
- Is Double: Find the first recurring character in a string.
Naive answer code
# Naive way takes O(n^2)
def isDouble_naive(str):
# For each 'i'th char, we check whether it occurs double
for i in range(len(str)):
for j in range(i+1, len(str)):
if str[i] == str[j]:
return str[i]
return None
Better way using ‘dictionary’
# Better way using dict takes O(n)
def isDouble_dict(str):
# Using dictionary (hash table)
ht = dict()
for c in str:
if c not in ht: # O(1) for average case, O(n) for worst case
ht[c]=1 # O(1)
else:
return c
return None
Better way using ‘set’
# Better way using set takes O(n)
def isDouble_set(str):
# Using dictionary (hash table)
ht = set()
for c in str:
if c not in ht: # O(1) for average case, O(n) for worst case
ht.add(c) # O(1)
else:
return c
return None
Quiz
- Is Unique: Implement an algorithm to determine if a string has all unique characters. What if you cannot use additional data structures?
Naive answer code
def isunique_naive(string):
for i in range(len(string)):
if string.find(string[i], i+1) != -1:
return False # Char is not unique
return True # All unique characters
Clever answer code
# O(N)
def isunique(string):
# Assuming character set is ASCII (128 characters)
if len(string) > 128:
return False
char_set = [False for _ in range(128)]
for char in string:
val = ord(char) # Char to ASCII
if char_set[val]:
return False # Char already found in string
char_set[val] = True
return True